METROM’s
Blog
METROM’s
Blog
Exploring Unique Features of Industrial 3D Printing Machines and Their Ideal Applications
In the rapidly evolving world of manufacturing, industrial 3D printing machines have emerged as a transformative force, offering unparalleled capabilities that push the boundaries of traditional production methods. These machines are not only revolutionizing how products are designed and fabricated but also opening up new possibilities across various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. However, the effectiveness of these advanced technologies greatly depends on choosing the right manufacturer. In this blog, we will explore the unique features of industrial 3D printing machines, highlighting their strengths and ideal applications. By understanding these characteristics, businesses can make informed decisions when selecting quality manufacturers that align with their operational needs and innovation goals. As we dive into the world of industrial 3D printing, we aim to equip readers with the knowledge necessary to navigate this complex landscape and harness the full potential of these groundbreaking machines.

Key Innovations in Industrial 3D Printing Technologies
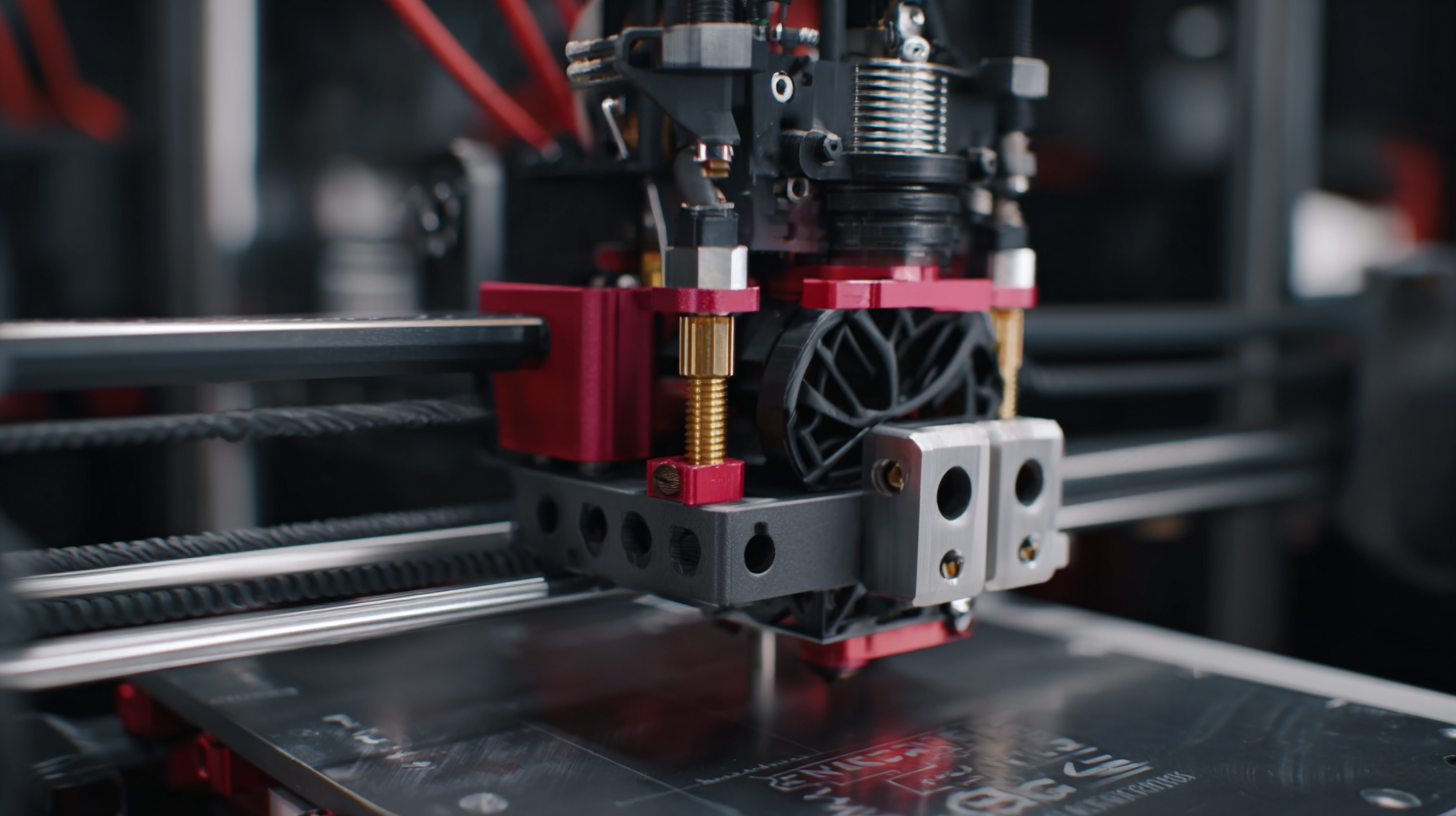 The advancements in industrial 3D printing technologies are revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape, allowing for unprecedented levels of customization and efficiency. One of the key innovations lies in the development of high-speed sintering processes, which enable manufacturers to create complex geometries at a fraction of the time required by traditional methods. This technology not only accelerates production but also reduces material waste, making it an ideal solution for industries where precision and sustainability are paramount.
The advancements in industrial 3D printing technologies are revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape, allowing for unprecedented levels of customization and efficiency. One of the key innovations lies in the development of high-speed sintering processes, which enable manufacturers to create complex geometries at a fraction of the time required by traditional methods. This technology not only accelerates production but also reduces material waste, making it an ideal solution for industries where precision and sustainability are paramount.
Another significant innovation is the emergence of multi-material printing, which allows for the integration of various materials into a single print. This capability opens up a world of possibilities for creating objects with tailored properties, such as flexible and rigid components within the same structure. Sectors like aerospace and automotive are particularly benefitting from this technology, as it helps in optimizing performance while reducing overall weight. As these innovations continue to evolve, they are set to unlock new applications and expand the horizons of industrial 3D printing, positioning it as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
Understanding Different Types of Industrial 3D Printers
Industrial 3D printing has transformed the manufacturing landscape, offering a variety of printers tailored for diverse applications. Among the different types of industrial 3D printers, Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) stand out. FDM printers are user-friendly and ideal for prototyping, making them a popular choice for startups and educational institutions. SLA printers, known for their high-resolution capabilities, are perfect for intricate designs in sectors such as jewelry and dental. Meanwhile, SLS printers excel in producing durable parts from powder materials, suitable for aerospace and automotive industries.
When selecting an industrial 3D printer, consider the material compatibility specific to your project. Each printer type is designed for different materials; FDM mainly uses thermoplastics, while SLA works with photopolymers. For those looking to invest in a versatile solution, hybrid printers that combine various technologies and materials could be the answer.
One crucial tip is to evaluate the volume and size of parts you need to produce. If large-scale components are your goal, look for printers with a substantial build size. Conversely, if precision is paramount, opt for printers known for their accuracy. Always conduct thorough research and possibly arrange demonstrations to find the best fit for your specific industrial needs.
Unique Features of Industrial 3D Printing Machines
Comparative Analysis of Material Capabilities in 3D Printing
The landscape of industrial 3D printing is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in material technology. This comparative analysis highlights the diverse material capabilities that define the effectiveness and application suitability of various 3D printing machines. According to a recent market study by SmarTech Analysis, thermoplastics and metal powders dominate the market, collectively accounting for over 70% of the materials used in industrial applications. Each material brings unique characteristics; for instance, nylon is favored for its flexibility and durability, while titanium powders are touted for their strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for aerospace components.
Furthermore, the introduction of bio-based materials is gaining attention, aligning with sustainability goals in manufacturing. According to a report from Wohlers Associates, the use of biodegradable materials in 3D printing is projected to increase by 25% over the next five years. This shift not only addresses environmental concerns but also opens up new avenues for applications in medical and consumer products, where bio-compatibility is paramount. Remember to stay updated on material innovations to harness their full potential in your 3D printing projects.
Evaluating Productivity and Speed Across Various Machines
Industrial 3D printing machines are revolutionizing manufacturing processes by offering unparalleled productivity and speed across different applications. When evaluating these machines, one important aspect is the build speed, which varies significantly based on the technology used. For instance, binder jetting machines excel at producing large volumes of parts quickly, making them ideal for applications such as sand casting and metal parts production. On the other hand, technologies like selective laser sintering (SLS) may offer slower build rates but compensate with exceptional material versatility and precision, suitable for aerospace components or intricate prototypes.
Another factor influencing productivity is the scalability of the machine's design. Machines equipped with multiple lasers can dramatically reduce printing times by enabling parallel processing, thereby catering to high-demand production environments. Furthermore, the implementation of advanced software for print optimization enhances workflow efficiency, allowing operators to schedule and manage multiple jobs seamlessly. As industries continue to adopt these innovative machines, understanding their strengths in terms of speed and productivity will be crucial for maximizing their potential in specific applications.
Exploring Unique Features of Industrial 3D Printing Machines and Their Ideal Applications
| Machine Type | Technology | Build Volume (mm) | Layer Height (mm) | Print Speed (mm/s) | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDM | Fused Deposition Modeling | 300 x 300 x 400 | 0.1 - 0.5 | 60 | Prototyping, Hobbyist Projects |
| SLA | Stereolithography | 200 x 200 x 300 | 0.025 - 0.1 | 30 | Jewelry, Dental Models |
| SLS | Selective Laser Sintering | 250 x 250 x 300 | 0.1 - 0.15 | 20 | Functional Parts, Aerospace |
| DLP | Digital Light Processing | 250 x 140 x 180 | 0.05 - 0.1 | 50 | Prototyping, Dental Applications |
| Binder Jetting | Binder Jetting | 400 x 250 x 200 | 0.1 - 0.5 | 100 | Metal Parts, High Volume Production |
Identifying Ideal Applications for Each Type of 3D Printing Technology
Industrial 3D printing technology encompasses a variety of methods, each with unique features that cater to different applications across multiple sectors. For instance, Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is celebrated for its cost-effectiveness and versatility, often used in prototyping and low-volume production. According to a recent Wohlers Report, FDM accounts for about 40% of the global 3D printing market, reflecting its widespread appeal in areas like automotive and consumer goods prototyping, where rapid iteration is essential.
On the other hand, Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) stands out for its ability to create complex geometries without the need for support structures, making it ideal for producing intricate parts in aerospace and medical applications. A 2022 study by IDTechEx highlighted that SLS technology is projected to grow significantly, with an estimated CAGR of 22% through 2028, driven by its suitability for small-batch production of functional parts. Each 3D printing technology, from Binder Jetting to Digital Light Processing (DLP), brings distinctive advantages that align with specific industry needs, showcasing the vast potential of 3D printing in enhancing manufacturing efficiency and innovation.


